BD139 Transistor Information
The BD139 is a popular NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) used in a variety of electronic circuits. It is typically used for amplification and switching applications in low-power devices. Below, I'll provide some key information about the BD139 transistor:
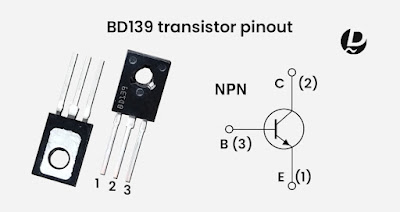
1. Pin Configuration:
The BD139 transistor typically comes in a TO-126 package. It has three pins: Collector (C), Base (B), and Emitter (E). The pinout is as follows:
- Emitter (E) - Pin 1
- Collector (C) - Pin 2
- Base (B) - Pin 3
2. Electrical Characteristics:
- Collector-Base Voltage (Vcb): 80V
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vce): 80V
- Emitter-Base Voltage (Vbe): 5V
- Collector Current (Ic): 1.5A
- Power Dissipation (Pd): 12.5W
- DC Current Gain (hfe): Typically around 40 to 250, depending on the specific part and biasing conditions.
- Transition Frequency (ft): Approximately 100MHz
3. Features:
- High current and voltage handling capabilities for its size.
- Suitable for small-signal amplification and switching applications.
- Can be used in a wide range of low to medium-power electronic circuits.
- Relatively low cost and widely available.
4. Typical Applications:
The BD139 transistor can be found in various electronic circuits, including but not limited to:
- Amplifiers: It's commonly used in audio amplifiers and low-frequency signal amplification.
- Switching Circuits: Used for switching applications in timer circuits, oscillators, and more.
- Voltage Regulators: It can be part of voltage regulator circuits.
- Signal Processing: It's used in signal processing and filtering circuits.
- LED Drivers: In some cases, it can be used to drive LEDs in small lighting applications.
Always consult the BD139 datasheet and ensure proper calculations and safety measures when using it in your circuit designs. The transistor's characteristics may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer, so refer to the datasheet for precise information.